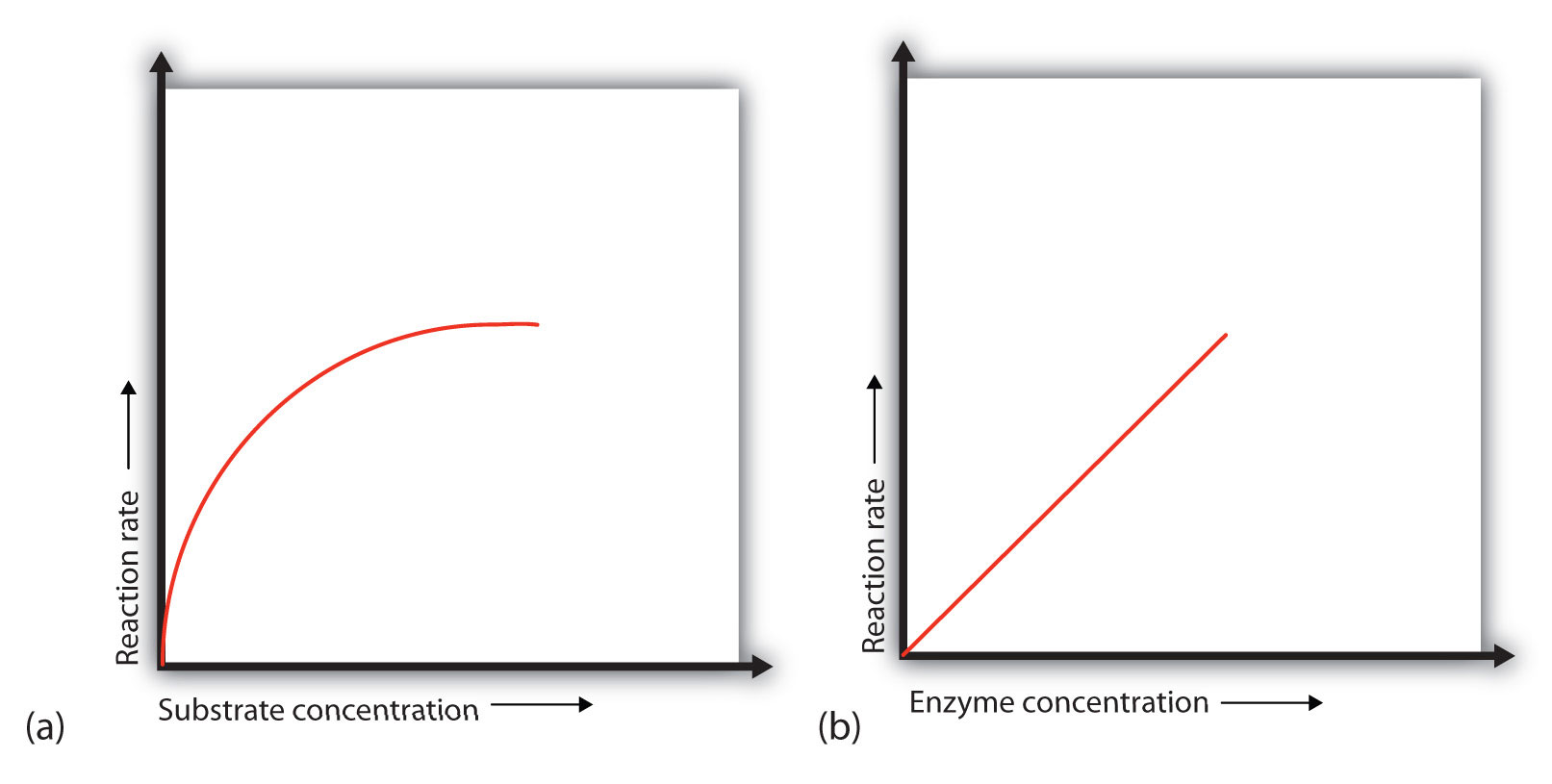
Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration . Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. In effect, they compete for the active.
from guides.hostos.cuny.edu
The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. In effect, they compete for the active. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive.
Chapter 9 Proteins and Enzymes CHE 120 Introduction to Organic
Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In effect, they compete for the active. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. In effect, they compete for the active. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme.
From alevelnotes.com
Enzyme Inhibitors A Level Notes Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
Chemistry for Biologists Enzymes Chemistry classroom, Enzymes Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Competitive, and Inhibition and Graph Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Chapter 3.3 Enzyme inhibition Competitive and Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.savemyexams.com
1.4.12 Limiting Factors Affecting Enzymes Inhibitors AQA A Level Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In effect, they compete for the active. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The Graph Below Shows Three Plots Of Velocity (v0)... Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.researchgate.net
The percentage of inhibition as a function of the concentration of the Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From chart-studio.plotly.com
Effect of Substrate Concentration on Enzyme Activity scatter chart Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In effect, they compete for the active. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.lecturio.com
Enzyme Inhibition Concise Medical Knowledge Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.vrogue.co
Enzyme Inhibition Mechanism vrogue.co Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.expii.com
Enzyme Inhibition — Overview & Types Expii Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.youtube.com
Competitive inhibition YouTube Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.animalia-life.club
Mixed Inhibition Graph Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. In effect, they compete for the active. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.lecturio.com
Enzyme Inhibition Concise Medical Knowledge Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases until a limiting rate. In a linked series of reactions, if the middle reaction is inhibited, the substrate for that enzyme builds, whether the inhibition is competitive or uncompetitive. In effect, they compete for the active. Competitive inhibition occurs. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.abpischools.org.uk
Enzyme inhibition Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In effect, they compete for the active. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. The effect of a competitive inhibitor depends on the inhibitor concentration, the substrate concentration and the relative affinities of the. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From guides.hostos.cuny.edu
Chapter 9 Proteins and Enzymes CHE 120 Introduction to Organic Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. In effect, they. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.coursehero.com
Energy, Matter, and Enzymes Microbiology Course Hero Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration In effect, they compete for the active. Competitive inhibition, in biochemistry, phenomenon in which a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly. In the presence of a given amount of enzyme, the rate of an enzymatic. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.
From www.dreamstime.com
Catalyst Competitive Inhibition Active Site Stock Vector Illustration Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration Competitive inhibition occurs when substrate (s) and inhibitor (i) both bind to the same site on the enzyme. Indeed, by increasing the substrate concentration from 20 µm to 200 µm, the inhibition curve shifted to the right and the ic 50. Probably the easiest type of enzyme inhibition to understand is competitive inhibition and it is the one most commonly.. Competitive Inhibition And Substrate Concentration.